INTRODUCTION
CD3 typically refers to Cluster of Differentiation 3. T cells have a combination of proteins on their cell surface called CD3. a type of immune cell involved in adaptive immune responses. It is essential for the growth, activation, and signaling of T cells. In both research and diagnostics, CD3 is frequently employed as a marker to distinguish and describe T cells.
Function CD3
When the T cell receptor (TCR) complex is activated, CD3 plays a crucial role in signal transmission. It is crucial for the activation of T cells, which triggers immunological reactions. To ensure optimal antigen recognition abilities, CD3 is crucial in T cell growth and maturation. Also known as a co-receptor, CD3 facilitates TCR binding to antigen-presenting cells for effective T cell activation.
Structure CD3
The CD3 complex consists of CD3γ, CD3δ, CD3ε, and CD3ζ subunits. CD3γ, CD3δ, and CD3ε form a heterodimeric complex with extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains. CD3ζ exists as a homodimer and contains extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic regions. The CD3 complex associates with the T cell receptor (TCR) α and β chains to form the functional TCR-CD3 complex on the surface of T cells. The cytoplasmic tails of CD3ε and CD3ζ contain immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs), which play a role in intracellular signaling upon TCR engagement.
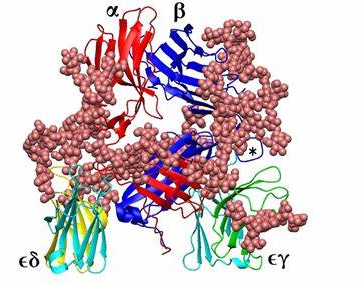
CD3 protein (epsilon /delta ectodomain dimer). CD3 is present on the surface of T-lymphocytes and is required for T-cell activation.
- The γ subunit of the CD3 complex is commonly known as CD3 gamma.
- The δ subunit of the CD3 complex is commonly known as the CD3 delta.
- The ε subunit of the CD3 complex is commonly referred to as CD3 epsilon.
- The ζ subunit of the CD3 complex is commonly referred to as CD3 zeta.
Function CD3 in the immune response
CD3 is responsible for transmitting intracellular signals upon T cell receptor (TCR) engagement, leading to T cell activation and initiation of immune responses. It plays a crucial role in T cell development, ensuring proper maturation and selection of functional T cells. CD3 acts as a co-receptor, enhancing TCR binding to antigen-presenting cells for efficient T-cell activation. CD3 is essential for T cell-mediated immune responses and immune system functionality.
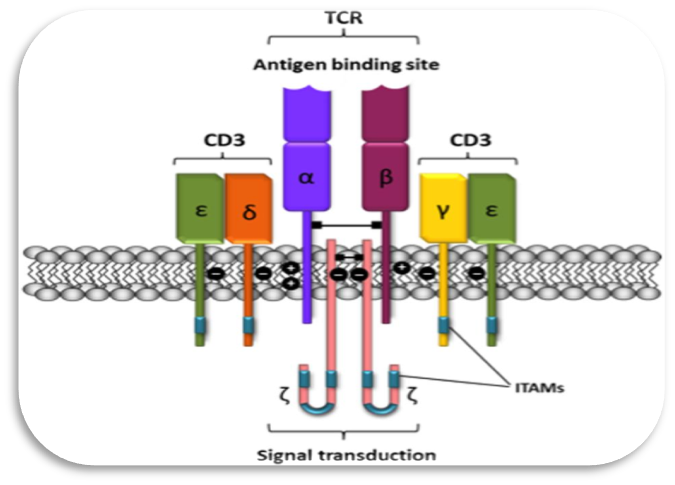
Schematic representation of the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. The heterocomplex is formed by variable TCR-α and TCR-β chains coupled to three dimeric signaling transduction modules CD3δ/ε, CD3γ/ε, and CD3ζ/ζ or CD247. CD3, Cluster of differentiation 3; CD247, a cluster of differentiation 247 or CD3ζ/ζ; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; TCR, T-cell receptor.
CD3 uses in annotations.
CD3 is used for annotations because it is a reliable marker specifically expressed on T cells. It enables accurate identification and annotation of T cells within tissue samples or cellular populations. CD3 staining aids in quantifying T cell numbers, assessing their distribution, and studying their role in diseases. Additionally, CD3 annotations offer important diagnostic and prognostic data as well as a way to track the success of targeted or immunotherapy treatments.
Detection and analysis
The following steps were taken to detect, assess, and annotate CD3 expression:
- Sample preparation: HeLa cells were treated with paraformaldehyde to preserve their structure and antigenicity. To allow antibody penetration into the cells, Triton X-100 was used to permeabilize the cells.
- Blocking: The cells were treated with a blocking solution containing 10% serum to reduce non-specific binding. This process reduces background staining and improves antibody binding selectivity.
- Incubation with antibodies: The cells were treated with a combination of two primary antibodies: mouse anti-beta tubulin and a polyclonal antibody against CD3/CD8 (Product # PA5-102404). A 1:200 dilution of the CD3/CD8 antibody was utilized. This primary antibody identifies just CD3 or CD8 proteins in the sample.
- After incubating with primary antibodies, the cells were tagged with secondary antibodies conjugated with fluorescent dyes. The CD3/CD8 antibody was detected using a goat anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 594 (red) antibody, while the beta-tubulin antibody was detected using a goat anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 488 (green).
- Imaging and analysis: Images of the stained cells were captured using a fluorescence microscope. The presence of CD3/CD8 is indicated by the red fluorescence, while beta tubulin is represented by the green fluorescence. The expression and localization of CD3/CD8 can be assessed by comparing and evaluating fluorescence signals.
- Annotation: Annotations can be established based on observed fluorescence patterns to identify CD3/CD8-positive cells or specific cellular areas where CD3/CD8 is located. This data can be utilized to further analyze and interpret the biological significance of CD3/CD8 in the experimental system.
HSA KIT SOFTWARE
By automating cell detection, enabling quantitative analysis of CD3 expression, providing annotation tools for marking CD3-positive cells, facilitating visualization of staining patterns, assisting in data management, providing advanced image processing algorithms, and improving the efficiency and accuracy of CD3 annotation tasks, HSA KIT software plays a critical role in making CD3 annotations.

The HS Analysis software is quite useful in assisting medical practitioners in detecting diseases. It allows them to diagnose and assess numerous medical disorders by evaluating high-resolution images of tissues and organs.
The HS Analysis touch
HS-analysis provides quality control and analysis services for raw materials and final products in a variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and agriculture. Chemical and physical testing, microbiological analysis, and stability testing are among the analytical services provided by the organization.
The latest artificial intelligence is a vital technology for the automatic interpretation of tissue samples in the HS Analysis program.
By evaluating high-resolution photographs of tissues and organs, the HS Analysis program can assist medical practitioners in diagnosing illnesses. And, when the program generates data characterizing the patient’s current health, it will aid doctors in picking the appropriate therapy.
The images below show the CD3 of HS Analysis KIT
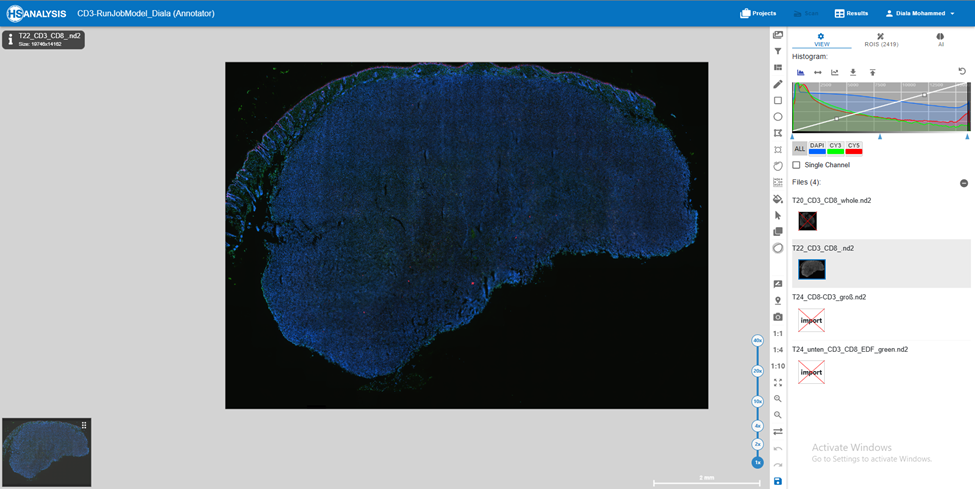
Follow these steps to create CD3 annotations in HSA KIT software:
- Open the image with the T-cell imaging or immunofluorescence staining that you want to annotate with CD3.
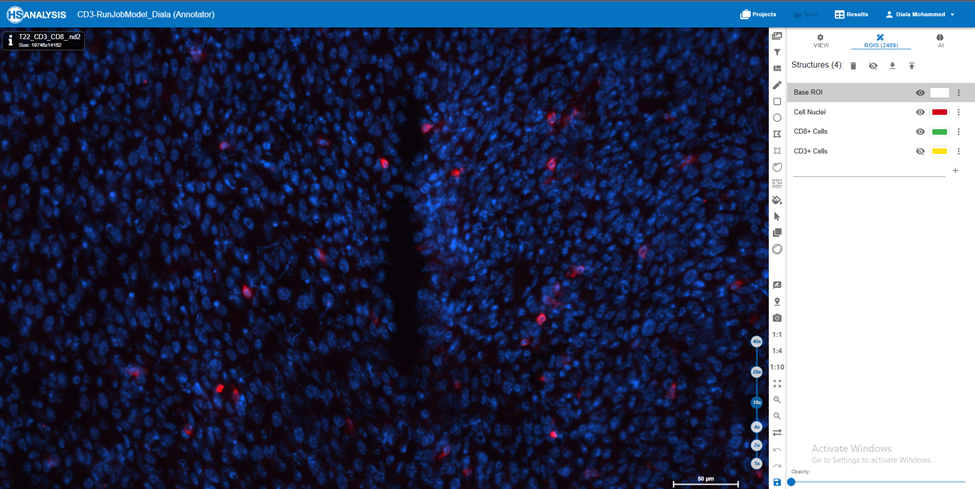
2. Using the software’s drawing tools, manually outline or trace the CD3-positive portions on the image. Annotations are often created using forms such as polygons, or circles.
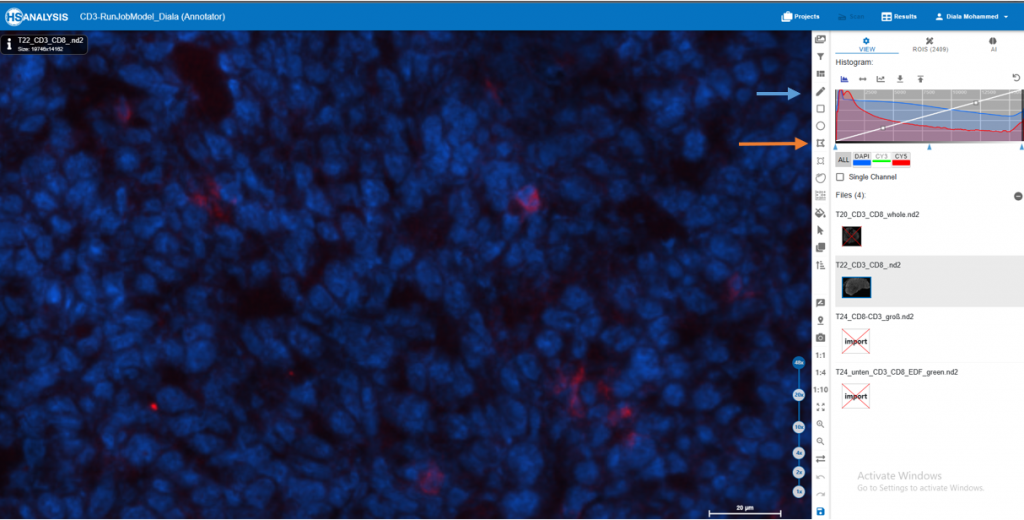
3. Within the software, locate the color channel settings or channels panel. You can adjust the visibility of specific color channels using this panel.
Find the blue color channel in the channels panel and turn it off. This will disable the blue color, rendering it invisible in the image.
Similarly, under the Channels panel, locate the red color channel and disable its appearance. This will disable the red color.
4. Check that the image now only shows the green color channel, which reflects the CD3 staining.
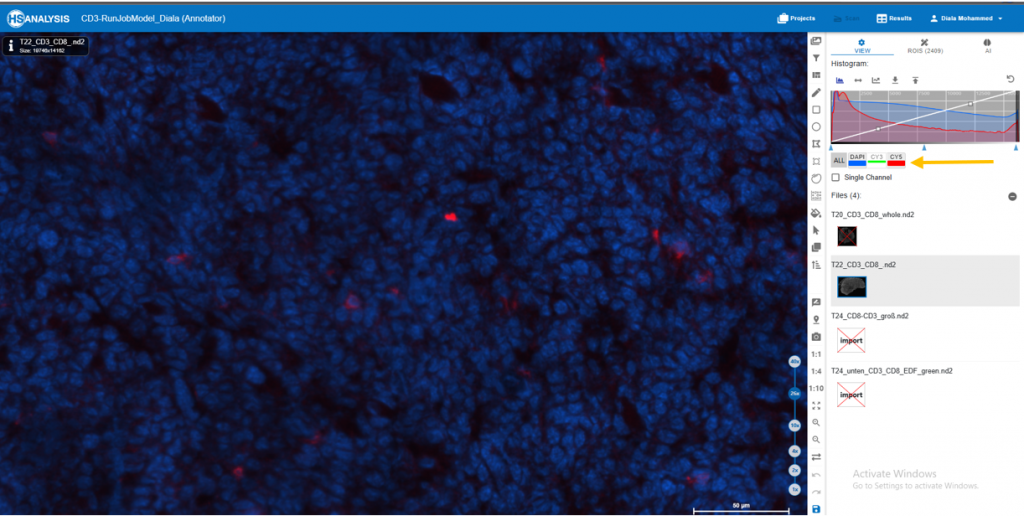
5. Using the appropriate annotation tools, create the desired annotations on the CD3-positive locations.
Show this video to clarify further.
Future Directions
For a better understanding of T-cell biology and disease-related insights, the future of image analysis for CD3 holds the potential for automation, AI-driven algorithms, high-throughput analysis, multiplexing and spatial analysis, deep learning-based segmentation, integration with omics data, and interactive visualization.
